Cindy and Her Husband Are Trying to Have a Baby. Based on the Calender Method of Birth Control
Your selection of a birth command method depends on a number of factors, including your health, how oftentimes y'all have sex, and whether or not y'all desire children.
Hither are some questions to consider when selecting a birth control method:
- How well does the method prevent pregnancy? To tell how well a method works, look at the number of pregnancies in 100 women using that method over a period of 1 year.
- What are your feelings nearly getting pregnant? Would an unplanned pregnancy create hardship or distress to a adult female or her partner? Or would a pregnancy be welcomed if it occurred earlier than planned?
- How much does a method of nativity control cost? Does your insurance programme pay for it?
- What are the health risks? Talk about these risks with your health care provider earlier believing what you hear from others.
- Is your partner willing to take and use a given method of nascency control?
- Do yous want a method that you simply need to use when you have sex? Or exercise you desire something that is in place and always working?
- Is preventing infections spread past sexual contact important? Many methods practice not protect you from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Condoms are the best pick for preventing STIs. They work all-time when combined with spermicides.
- Availability: Can the method be used without a prescription, a provider visit, or, in the case of minors, parental consent?
Barrier METHODS OF Nascency Control
CONDOMS:
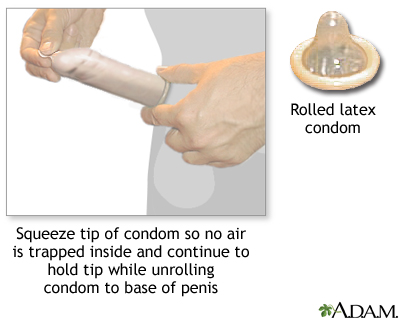
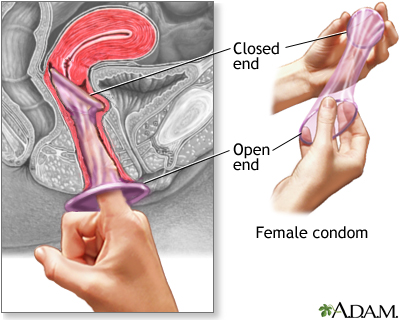
- A condom is a thin latex or polyurethane sheath. The male condom is placed around the erect penis. The female condom is placed within the vagina before intercourse.
- A safe must exist worn at all times during intercourse to prevent pregnancy.
- Condoms can be bought in near drug and grocery stores. Some family unit planning clinics offering costless condoms. You do not need a prescription to get condoms.
DIAPHRAGM AND CERVICAL CAP:
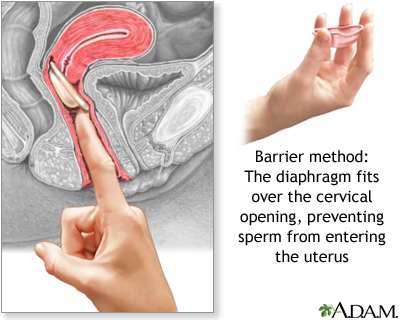
- A diaphragm is a flexible rubber cup that is filled with spermicidal cream or jelly.
- Information technology is placed into the vagina over the neck before intercourse, to prevent sperm from reaching the uterus.
- It should exist left in identify for vi to 8 hours later intercourse.
- Diaphragms must be prescribed by a woman's provider. The provider volition determine the right type and size of diaphragm for the woman.
- Near 5 to twenty pregnancies occur over 1 year in 100 women using this method, depending on proper use.
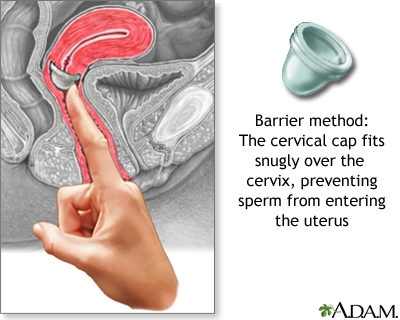
- A similar, smaller device is called a cervical cap.
- Risks include irritation and allergic reactions to the diaphragm or spermicide, and increased frequency of urinary tract infection and vaginal yeast infection. In rare cases, toxic shock syndrome may develop in women who exit the diaphragm in likewise long. A cervical cap may crusade an abnormal Pap examination.
VAGINAL SPONGE:
- Vaginal contraceptive sponges are soft, and contain a chemic that kills or "disables" sperm.
- The sponge is moistened and inserted into the vagina, to encompass over the cervix before intercourse.
- The vaginal sponge tin can be bought at your pharmacy without a prescription.
HORMONAL METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
Some nativity control methods use hormones. They volition have either both an estrogen and a progestin, or a progestin alone. You need a prescription for most hormonal birth control methods.
- Both hormones foreclose a woman'due south ovary from releasing an egg during her cycle. They do this by affecting the levels of other hormones the body makes.
- Progestins help prevent sperm from making their mode to the egg by making fungus around a woman'southward cervix thick and sticky.
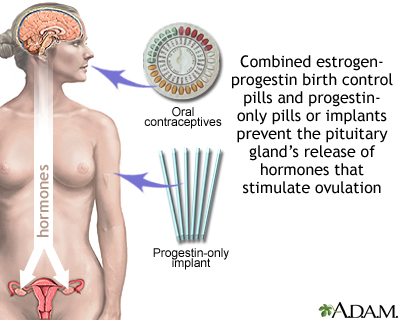
Types of hormonal birth control methods include:
- Birth command pills: These may incorporate both estrogen and progestin, or merely progestin.
- Implants: These are small rods implanted beneath the pare. They release a continuous dose of hormone to prevent ovulation.
- Progestin injections, such equally Depo-Provera, that are given into the muscles of the upper arm or buttocks once every 3 months.
- The skin patch, such as Ortho Evra, is placed on your shoulder, buttocks, or other place on the trunk. Information technology releases a continuous dose of hormones.
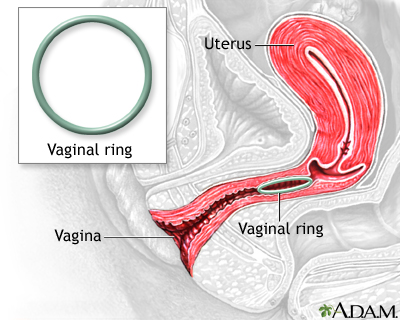
- The vaginal ring, such as NuvaRing, is a flexible ring about 2 inches (five centimeters) broad. It is placed into the vagina. It releases the hormones progestin and estrogen.
- Emergency (or "morning after") contraception: This medicine can be bought without a prescription at your drugstore.
IUD (INTRAUTERINE DEVICE):
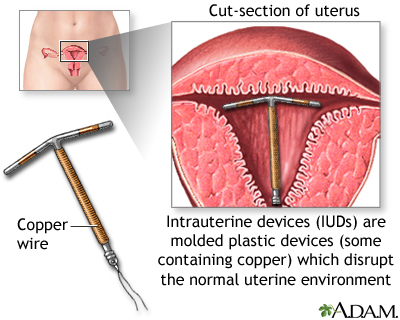
- The IUD is a small-scale plastic or copper device placed inside the adult female's uterus by her provider. Some IUDs release small amounts of progestin. IUDs may exist left in place for three to 10 years, depending on the device used.
- IUDs tin exist placed at most any time.
- IUDs are safe and piece of work well. Fewer than 1 out of 100 women per year will get pregnant using an IUD.
- IUDs that release progestin may be for treating heavy menstrual bleeding and reducing cramps. They may as well cause periods to stop completely.
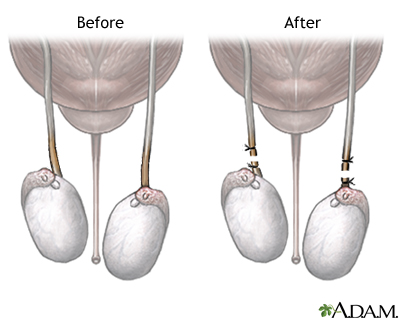
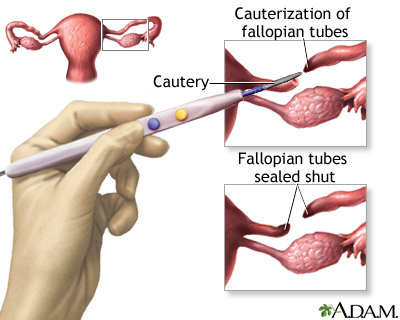
PERMANENT METHODS OF BIRTH CONTROL
These methods are all-time for men, women, and couples who feel certain they do not want to accept children in the future. They include vasectomy and tubal ligation. These procedures can sometimes exist reversed if a pregnancy is desired at a afterward fourth dimension. However, the success rate for reversal is non loftier.
BIRTH Control METHODS THAT DO NOT Work VERY WELL
- Withdrawal of the penis from the vagina before ejaculation can still result in pregnancy. Some semen often escapes before full withdrawal. It can be plenty to cause a pregnancy.
- Douching before long after sex activity is not likely to work. The sperm can make their way past the cervix inside 90 seconds. Douching is never recommended because information technology tin cause infections in the uterus and tubes.
- Breastfeeding: Despite the myths, women who are breastfeeding can become meaning.
Contraception; Family planning and contraception; Coitus interruptus
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Do Bulletin No. 206: Apply of hormonal contraception in women with circumstantial medical conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(ii):396-399. PMID : 30681537 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30681537/.
Committee on Adolescent Health Care. Committee Stance No 699: Adolescent pregnancy, contraception, and sexual activity. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129(5):e142-e149. PMID: 28426620 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28426620/.
Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. US selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(iv):1-66. PMID: 27467319 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27467319/.
Harper DM, Wilfling LE, Blanner CF. Contraception. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 26.
Jatlaoui TC, Ermias Y, Zapata LB. Contraception. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 143.
Rivlin Thousand, Westhoff C. Family planning. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Managing director, and the A.D.A.Thousand. Editorial team.
Source: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001946.htm
Post a Comment for "Cindy and Her Husband Are Trying to Have a Baby. Based on the Calender Method of Birth Control"